Cover
This comprehensive dental handbook, updated as of 01/22/2026, provides essential clinical guidance, covering history, examination, and restorative techniques for practitioners.
Title Page
Handbook of Modern Dental Practice – a meticulously crafted resource designed for dental professionals and students alike. This edition, reflecting updates through December 17, 2025, integrates the latest advancements in restorative dentistry, periodontology, orthodontics, and pediatric care.
It encompasses vital information on nitrous oxide sedation, endodontics, and a detailed exploration of dental anatomy and histology. Supporting Australia’s National Oral Health Plan, including the Child Dental Benefits Schedule (CDBS), this handbook serves as a cornerstone for comprehensive patient care and continued professional development.
Copyright Information
© 2026 by Dental Publishing Group. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including photocopying, recording, or other electronic or mechanical methods, without the prior written permission of the publisher.
Contents
This handbook details essential dental knowledge, from foundational history and examination techniques to advanced restorative and orthodontic procedures, as outlined in the table of contents.
Table of Contents Overview
This dental handbook’s structure begins with foundational elements – the Cover, Title Page, and Copyright information – followed by a detailed Contents section and a list of Contributors. Subsequent sections systematically explore core dental disciplines. These include History & Examination, Preventive Dentistry, Paediatric Dentistry, and Orthodontics.
Restorative dentistry is comprehensively covered across three parts: Periodontology, Repairing Teeth, and Replacing Teeth. Finally, Endodontics completes the clinical focus. The handbook also includes valuable Additional Resources, such as sedation guides and anatomical texts, supporting practical application and continued learning.
List of Contributors
While a specific list isn’t provided in the available data, this handbook benefits from the collective expertise of leading dental professionals and educators. Contributors specialize in diverse fields, including periodontology, orthodontics, endodontics, and paediatric dentistry.
Their combined clinical experience and academic rigor ensure the handbook’s content is both current and practical. Further details regarding individual contributor affiliations and qualifications will be found within the printed edition, acknowledging their vital role in shaping this comprehensive resource.
Symbols and Abbreviations
This section details commonly used dental symbols and frequently encountered abbreviations, ensuring clear communication and standardized record-keeping throughout the handbook.
Common Dental Symbols
Understanding standardized dental symbols is crucial for accurate charting and communication among dental professionals. This handbook utilizes universally recognized symbols to represent various dental features and conditions. For instance, a small circle often denotes caries, while a shaded triangle indicates a filling. Symbols are also employed to illustrate root morphology, furcation involvement, and the presence of restorations like crowns or implants.
Consistent use of these symbols ensures clarity in patient records, treatment planning, and radiographic interpretations. This section provides a detailed key to these symbols, facilitating efficient and unambiguous documentation within the clinical setting, promoting better patient care.
Frequently Used Abbreviations
Dental practice relies heavily on abbreviations for concise record-keeping and efficient communication. This handbook includes a comprehensive list of commonly used dental abbreviations to aid understanding and prevent misinterpretation. Examples include “DO” for Doctor of Orthodontics, “RCT” for Root Canal Treatment, and “PD” representing Probing Depth.
Familiarity with these abbreviations is essential for all dental team members. Utilizing a standardized set of abbreviations minimizes errors and streamlines workflows, ultimately enhancing the quality of patient care and ensuring accurate documentation within the clinical environment.
1 History and Examination
Effective patient care begins with a detailed dental history and a thorough clinical examination, as outlined starting on page 14 of this handbook.
Taking a Comprehensive Dental History
A thorough dental history, beginning on page 14, is paramount for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. This involves detailed questioning regarding the patient’s chief complaint, past dental experiences, medical history – including current medications and allergies – and social habits like smoking or bruxism.
Furthermore, explore family dental history, as certain conditions can be hereditary. Document any anxieties or fears the patient may have regarding dental treatment. A well-documented history forms the foundation for personalized and effective dental care, ensuring patient safety and optimal outcomes.
Performing a Thorough Clinical Examination
Following a detailed history (starting on page 14), a comprehensive clinical examination is crucial. This includes extraoral assessments – noting facial symmetry, lymph nodes, and temporomandibular joint function – and intraoral examination. Evaluate soft tissues for lesions, and hard tissues for caries, fractures, and restorations.
Record periodontal probing depths, assess tooth mobility, and document any existing restorations. Radiographic examination is integral for detecting hidden pathology. Accurate documentation of all findings is essential for diagnosis and treatment planning.
2 Preventive and Community Dentistry
This section, beginning on page 36, details caries prevention strategies and explores vital community dental health programs, like the Child Dental Benefits Schedule.
Dental Caries Prevention Strategies
Effective caries prevention, a cornerstone of dental practice, encompasses a multifaceted approach detailed within this handbook. Strategies include meticulous oral hygiene instruction, emphasizing proper brushing and flossing techniques. Dietary modifications, limiting sugary snacks and drinks, are crucial.
Fluoride therapies, such as topical applications and fluoridated water, strengthen enamel. Pit and fissure sealants provide a physical barrier against decay. Regular dental check-ups enable early detection and intervention, minimizing the progression of caries and preserving dental health for patients of all ages.
Community Dental Health Programs
This handbook highlights the importance of accessible dental care through robust community programs. Initiatives like the Child Dental Benefits Schedule (CDBS) in Australia exemplify efforts to improve oral health equity, providing financial assistance for eligible children’s dental treatments.
Public health campaigns promoting oral hygiene and preventative care are vital. Collaboration between dental professionals, schools, and community organizations expands reach. Addressing health literacy ensures effective communication of dental health messages, fostering a healthier population overall.
3 Paediatric Dentistry
This section details specialized dental care for infants and children, including trauma management and preventative strategies, ensuring optimal oral health development.
Dental Care for Infants and Children
Establishing positive oral hygiene habits early is crucial. This involves gentle cleaning of gums even before teeth erupt, progressing to soft-bristled toothbrushes with fluoride toothpaste as teeth appear.
Regular dental check-ups, starting with the first tooth’s emergence, are vital for monitoring development and preventing early childhood caries. Dietary guidance, limiting sugary drinks and snacks, plays a significant role.
The Child Dental Benefits Schedule (CDBS) in Australia offers financial assistance for eligible children’s dental care, promoting access to necessary treatments and preventative services.
Management of Childhood Dental Trauma
Prompt and appropriate management of dental trauma in children is essential to maximize the potential for successful healing and preserve tooth structure. Common injuries include fractures, luxations, and avulsions.
Immediate intervention, such as reimplantation of avulsed teeth within a specific timeframe, significantly impacts the prognosis. Stabilization splints may be necessary for luxated teeth.
Careful monitoring for complications like pulp necrosis is crucial, potentially requiring endodontic treatment.

4 Orthodontics
This section details orthodontic principles and treatment modalities, encompassing various appliance types for correcting malocclusion and achieving optimal dental alignment.
Principles of Orthodontic Treatment
Orthodontic treatment fundamentally aims to align teeth and jaws, improving both function and aesthetics. This involves understanding biomechanical principles – applying controlled forces to guide tooth movement.
Key considerations include diagnosis through clinical examination and radiographic analysis, followed by a carefully planned treatment strategy.
Successful outcomes rely on precise appliance selection, regular monitoring, and patient cooperation.
Treatment phases often involve initial alignment, space closure, and finishing stages to achieve a stable and harmonious occlusion.
Types of Orthodontic Appliances
A diverse range of orthodontic appliances exists, tailored to specific treatment needs. Traditional fixed appliances, utilizing brackets and wires, remain widely used for comprehensive correction.
Removable appliances, like aligners, offer aesthetic advantages and are suitable for milder cases.
Functional appliances influence jaw growth, often employed in growing patients.
Retainers are crucial post-treatment, preventing relapse and maintaining the achieved alignment.
Specialized appliances address specific issues, such as impacted teeth or temporomandibular joint disorders.
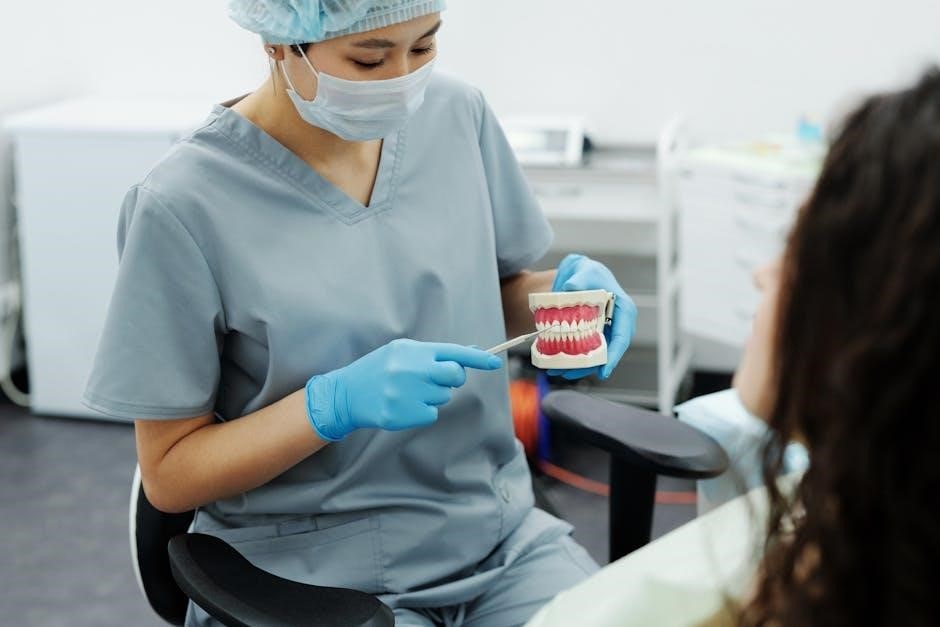
5 Restorative Dentistry 1: Periodontology
This section details periodontal diseases, focusing on understanding their etiology and progression, alongside effective non-surgical therapeutic interventions for optimal gum health.
Understanding Periodontal Diseases
Periodontal diseases encompass a spectrum of inflammatory conditions affecting the supporting tissues of the teeth, ultimately leading to potential tooth loss if left untreated. This handbook section explores the etiology, ranging from bacterial biofilm accumulation to host-mediated inflammatory responses.
We delve into the classification of periodontal diseases, including gingivitis and periodontitis, detailing their clinical presentations and radiographic features. Understanding risk factors – such as smoking, diabetes, and genetic predisposition – is crucial for effective prevention and management.
Furthermore, this section emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis through thorough clinical examination and appropriate diagnostic tools, paving the way for tailored treatment plans.
Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy
This section details the foundational principles of non-surgical periodontal therapy, aiming to control bacterial infection and halt disease progression without invasive procedures. Mechanical debridement, including scaling and root planing, forms the cornerstone of treatment, removing plaque and calculus from tooth surfaces.
Adjunctive therapies, such as antimicrobial irrigation and local delivery systems, enhance treatment efficacy by targeting persistent pathogens. Patient education regarding oral hygiene practices – brushing, flossing, and interdental cleaning – is paramount for long-term success.
Regular maintenance appointments are essential to monitor periodontal health and prevent recurrence.

6 Restorative Dentistry 2: Repairing Teeth
This chapter focuses on restoring damaged teeth using direct and indirect methods, ensuring functionality and aesthetics, as detailed within this dental handbook.
Direct Restorations (Fillings)
Direct restorations, commonly known as fillings, are crucial for repairing teeth damaged by decay or minor fractures. This handbook details material selection – including composite resins, glass ionomers, and amalgams – based on clinical needs and patient factors.
Proper cavity preparation, isolation techniques, and bonding protocols are emphasized for long-lasting restorations. The text also covers techniques for managing complex cases, such as deep caries or proximal restorations, ensuring optimal outcomes and patient comfort.
Indirect Restorations (Inlays, Onlays, Crowns)
Indirect restorations – inlays, onlays, and crowns – offer durable solutions for extensively damaged teeth. This handbook comprehensively explores material options like porcelain, zirconia, and metal alloys, detailing their respective strengths and indications.
Precise impression techniques, laboratory communication, and cementation procedures are thoroughly explained. The guide also addresses the management of complex cases, including endodontically treated teeth and fractured restorations, ensuring predictable and aesthetic results for patients.
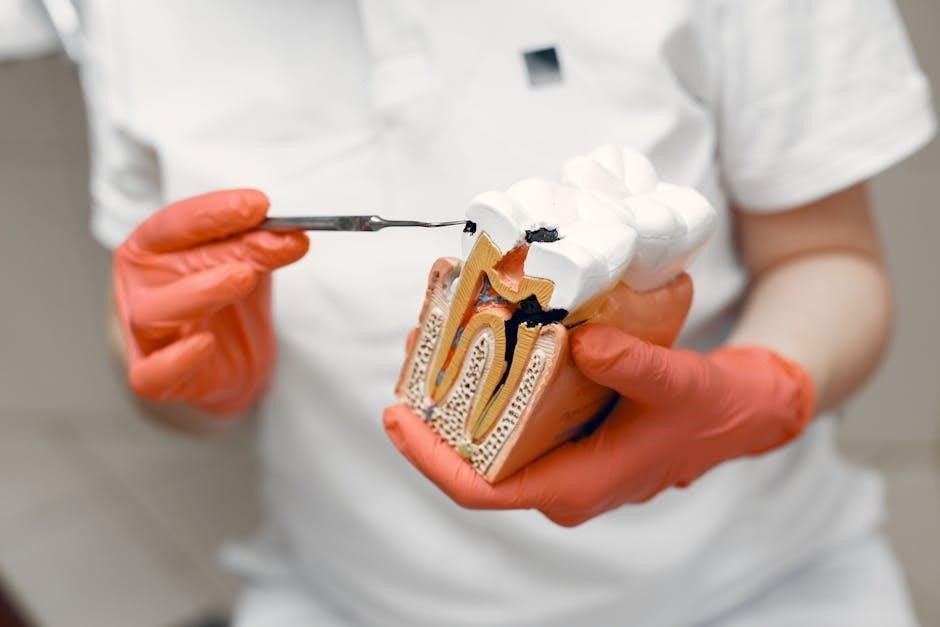
7 Restorative Dentistry 3: Replacing Teeth
This section details tooth replacement options, including dental implants and removable partial dentures, crucial for restoring function and aesthetics.
Dental Implants
Dental implants represent a premier long-term solution for tooth replacement, offering stability and functionality closely mimicking natural teeth. This handbook section comprehensively explores implant procedures, from initial assessment and surgical placement to prosthetic restoration.
Detailed coverage includes implant types, biocompatible materials, and considerations for successful osseointegration. Furthermore, it addresses potential complications, maintenance protocols, and the latest advancements in implant dentistry, ensuring practitioners have a robust understanding of this restorative option.
Removable Partial Dentures
Removable Partial Dentures (RPDs) provide a cost-effective solution for replacing missing teeth when implants or fixed bridges aren’t suitable. This handbook section details RPD design, fabrication, and fitting, emphasizing the importance of accurate impressions and proper support structures.
It covers various clasp designs, base materials, and considerations for maintaining oral hygiene and preventing tissue irritation. Furthermore, it addresses potential challenges like denture instability and the need for regular adjustments to ensure patient comfort and function.
8 Restorative Dentistry 4: Endodontics
This section details root canal treatment procedures and post-endodontic restoration, referencing resources like Hartys Endodontics in Clinical Practice, 7th edition.
Root Canal Treatment Procedure
The root canal procedure, a cornerstone of endodontic care, involves carefully removing infected or inflamed pulp from within the tooth. This handbook details accessing the pulp chamber, meticulous cleaning and shaping of the root canals, and subsequent obturation—filling the canals to prevent reinfection.
Proper diagnosis, utilizing radiographs and clinical examination, is crucial before initiating treatment. The procedure aims to alleviate pain, save the tooth, and restore its function. Resources like Hartys Endodontics in Clinical Practice offer detailed guidance on techniques and materials.
Post-Endodontic Restoration
Following successful root canal treatment, restoring the tooth to its full function and strength is paramount. This handbook emphasizes the importance of coronal sealing to prevent bacterial leakage into the root canal system.
Options range from direct restorations like fillings to indirect restorations such as crowns, depending on the extent of tooth structure loss. Careful consideration of occlusal forces and material selection, guided by resources like Hartys Endodontics, ensures long-term success.
Additional Resources
This handbook is complemented by texts on sedation, endodontics, histology, anatomy, and embryology, aiding comprehensive dental knowledge and clinical practice.
Nitrous Oxide and Oxygen Sedation Handbook
A crucial resource for dental professionals, the 5th edition of the Nitrous Oxide and Oxygen Sedation Handbook details safe and effective techniques for patient anxiety management.
It covers equipment, administration protocols, potential complications, and emergency procedures, ensuring practitioners are well-prepared to utilize this valuable tool.
Understanding proper patient assessment and monitoring is emphasized, alongside guidelines for maintaining a comfortable and secure environment during sedation.
Dental Anatomy and Histology Texts
Essential for a foundational understanding, several texts support dental education, including the 8th edition of Histology ౼ A Text and Atlas with Correlated Cell and Molecular Biology.
Further resources include Human Histology: A Text and Atlas for Physicians and Scientists, providing detailed microscopic views of dental tissues.
Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck (5th edition) and Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy complete the anatomical knowledge base.